Introduction
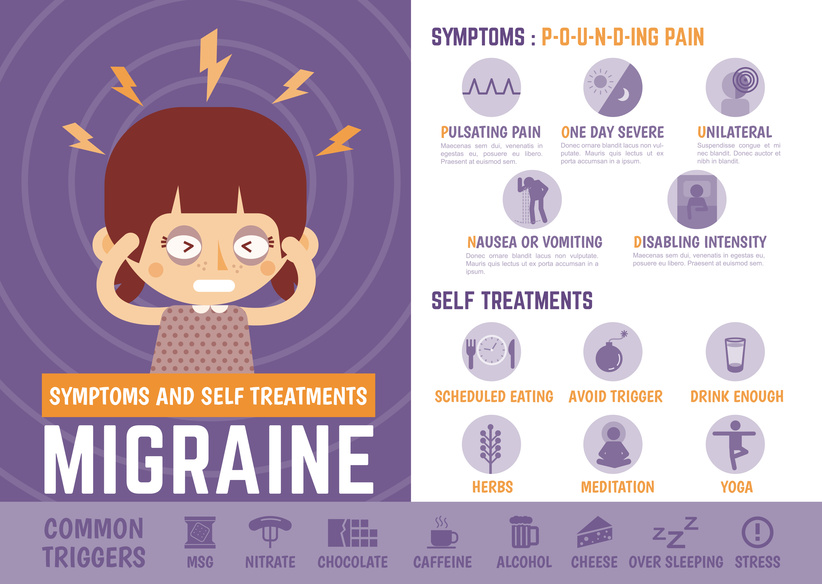
Migraine is a common and debilitating neurological disorder that affects millions of people around the world. It is characterized by recurrent episodes of moderate to severe headache pain, often accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound. While migraines can occur at any age, they are most common in adults between the ages of 25 and 55. In this article, we will explore the triggers that can cause chronic or high-frequency migraines.
What Are Chronic or High-Frequency Migraines?
Chronic or high-frequency migraines are defined as headaches that occur more than 15 days per month for at least three months. They can be disabling and significantly impact a person's quality of life. The exact causes of chronic or high-frequency migraines are not fully understood, but it is believed that they may be related to changes in brain chemicals and nerve pathways.
Common Triggers of Chronic or High-Frequency Migraines
There are several triggers that can increase the likelihood of chronic or high-frequency migraines. These include:
Stress
Stress is a common trigger for migraines. It can cause the body to release certain chemicals that can affect the brain and lead to a headache. Stress can come from a variety of sources, including work, relationships, financial concerns, and health problems.
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comHormonal Changes
Hormonal changes, particularly in women, can trigger migraines. These changes can occur during menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause. Birth control pills and hormone replacement therapy can also increase the risk of migraines in some women.
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comFood Triggers
There are several foods that can trigger migraines in some people. These include processed foods, cured meats, aged cheeses, chocolate, and alcohol. It is important to identify any food triggers and avoid them to reduce the frequency and severity of migraines.
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comSleep Disruption
Disruptions in sleep patterns can trigger migraines. This can include getting too much or too little sleep, irregular sleep schedules, and disruptions in sleep quality. Establishing a consistent sleep routine and practicing good sleep hygiene can help reduce the frequency of migraines.
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comEnvironmental Triggers
Environmental triggers can also contribute to chronic or high-frequency migraines. These can include changes in weather, exposure to bright or flashing lights, and strong odors such as perfumes or cleaning products.
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comConclusion
Chronic or high-frequency migraines can be debilitating and significantly impact a person's quality of life. By identifying and avoiding triggers, it is possible to reduce the frequency and severity of migraines. If you are experiencing chronic or high-frequency migraines, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of treatment.
No comments:
Post a Comment