 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comHeadaches are a common ailment that many people experience at some point in their lives. However, some individuals experience migraines, which are a specific type of headache that often comes with additional symptoms. Understanding the terminology associated with migraines and headaches can help individuals better manage their symptoms and seek appropriate treatment. In this article, we will explore a glossary of terms related to migraines and headaches.
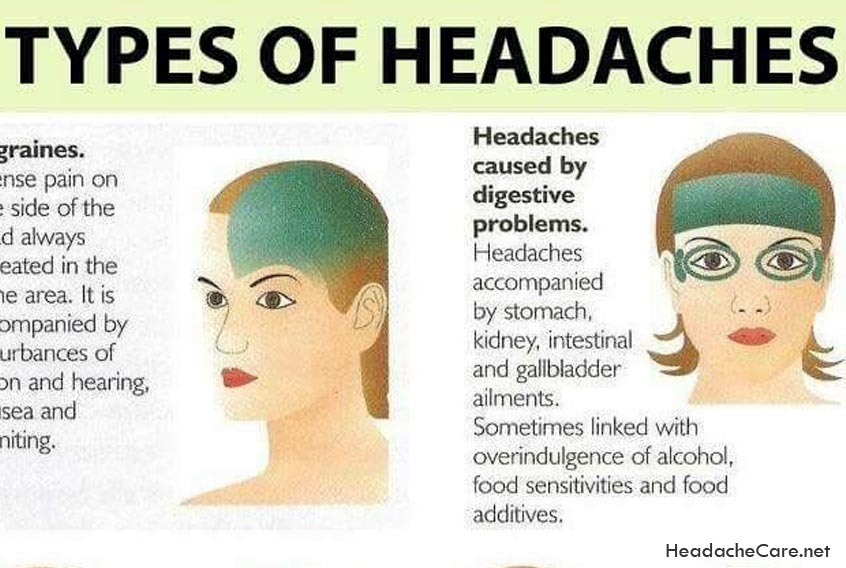
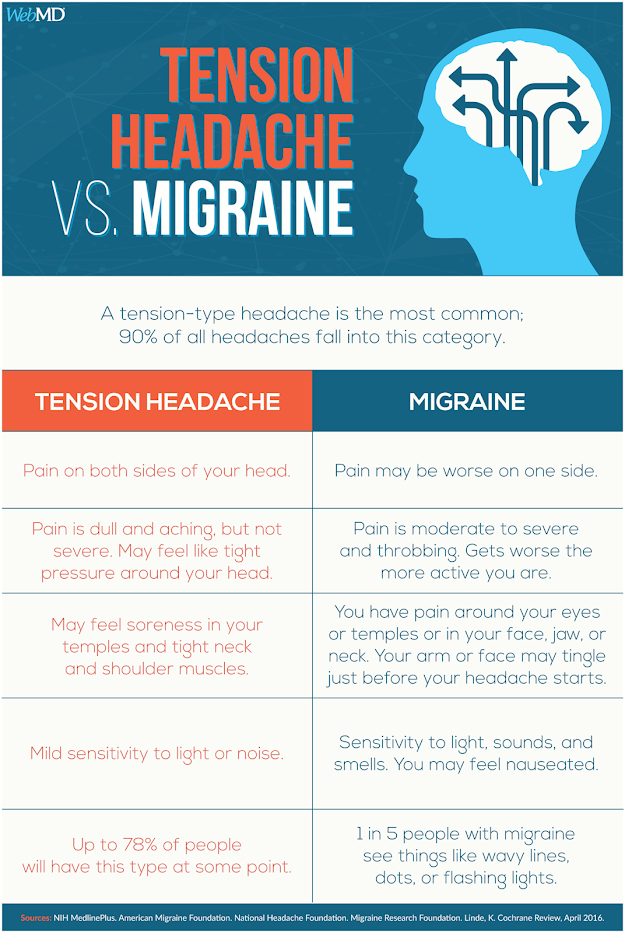
Migraine
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comMigraine is a neurological condition that causes moderate to severe headaches. These headaches typically affect only one side of the head and can last for several hours or even days. Migraines can also come with additional symptoms, such as nausea, sensitivity to light and sound, and visual disturbances. Migraines can be triggered by a variety of factors, including stress, hormonal changes, and certain foods.
Aura
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comAura is a term used to describe the visual disturbances that some individuals experience before a migraine headache. These disturbances can include seeing flashing lights, zigzag lines, or blind spots in their vision. Aura can also cause other sensory disturbances, such as tingling or numbness in the face or hands.
Chronic Migraine
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comChronic migraine is a term used to describe individuals who experience migraines on a frequent basis. Specifically, chronic migraine is defined as having headaches on 15 or more days per month, with at least eight of those days being migraines. Chronic migraines can be challenging to manage and often require a combination of medications and lifestyle changes.
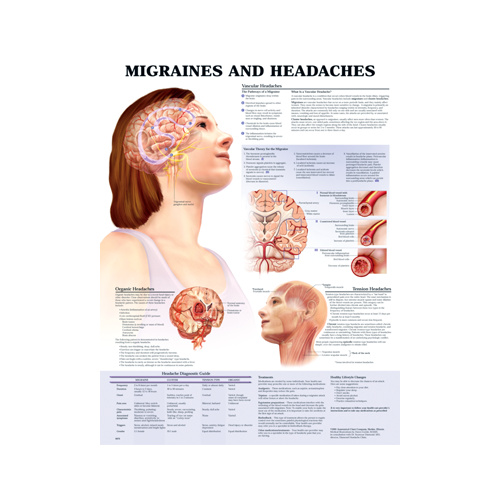
Cluster Headaches
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comCluster headaches are a type of headache that typically affects only one side of the head and come in clusters that can last for weeks or even months. These headaches are often described as a sharp, burning pain behind or around the eye. Cluster headaches can be incredibly painful and often require medical intervention to manage.
Tension Headaches
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comTension headaches are a type of headache that is often described as a constant, dull ache on both sides of the head. They are typically caused by muscle tension or stress and can last for several hours or days. Tension headaches are the most common type of headache and can often be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers.
Migraine Headache
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comA migraine headache is a specific type of headache that is characterized by moderate to severe pain on one side of the head. These headaches can last for several hours or days and often come with additional symptoms, such as nausea, sensitivity to light and sound, and visual disturbances. Migraine headaches can be triggered by a variety of factors, including stress, hormonal changes, and certain foods.
Occipital Nerve Stimulation
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comOccipital nerve stimulation is a type of therapy that involves implanting a device under the skin that sends electrical impulses to the occipital nerves in the back of the head. This therapy is often used to treat chronic migraine and can help reduce the severity and frequency of headaches.
Migraine Trigger
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comA migraine trigger is a specific factor that can cause or exacerbate a migraine headache. Some common migraine triggers include stress, lack of sleep, hormonal changes, and certain foods or drinks. Identifying and avoiding triggers can help individuals better manage their migraines.
Prodrome
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comProdrome is a term used to describe the early, pre-headache phase of a migraine. During this phase, individuals may experience a variety of symptoms, such as fatigue, mood changes, and food cravings. Recognizing the prodrome phase can help individuals better manage their migraines and take steps to prevent the headache from occurring.
Refractory Headaches
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comRefractory headaches are headaches that are resistant to treatment. These headaches can be incredibly challenging to manage and often require specialized care from headache specialists. Refractory headaches can be caused by a variety of factors, including medication overuse and underlying medical conditions.
Analgesic Rebound Headache
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comAnalgesic rebound headache is a type of headache that is caused by overusing pain medications. This type of headache is often described as a constant, dull ache that is resistant to treatment. Managing analgesic rebound headaches often involves slowly tapering off pain medications under the supervision of a medical professional.
Migraine with Aura
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comMigraine with aura is a specific type of migraine that comes with visual disturbances before the headache. These disturbances can include seeing flashing lights, zigzag lines, or blind spots in their vision. Migraine with aura can also cause other sensory disturbances, such as tingling or numbness in the face or hands.
Silent Migraine
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comSilent migraine is a type of migraine that comes with symptoms other than a headache. These symptoms can include visual disturbances, nausea, and sensitivity to light and sound. Silent migraines can be challenging to diagnose and manage, as they do not always come with a headache.
Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgia
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comTrigeminal autonomic cephalalgia is a group of headache disorders that come with autonomic symptoms, such as tearing, redness of the eye, and nasal congestion. These headaches typically affect one side of the head and can be incredibly painful. Trigeminal autonomic cephalalgia includes several subtypes, including cluster headaches and paroxysmal hemicranias.
Ocular Migraine
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comOcular migraine is a type of migraine that affects the vision in one eye. This type of migraine can cause temporary blindness or other visual disturbances, such as seeing flashing lights or zigzag lines. Ocular migraines typically last for less than an hour and often do not come with a headache.
Hemiplegic Migraine
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comHemiplegic migraine is a rare type of migraine that comes with temporary paralysis or weakness on one side of the body. This type of migraine can be challenging to manage and often requires specialized care from headache specialists.
Post-Traumatic Headache
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comPost-traumatic headache is a type of headache that is caused by a head injury, such as a concussion. These headaches can be challenging to manage and often require a combination of medications and lifestyle changes. Post-traumatic headaches can also come with additional symptoms, such as dizziness and memory problems.
Thunderclap Headache
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comThunderclap headache is a type of headache that comes on suddenly and is described as the worst headache of a person's life. These headaches can be indicative of a serious underlying condition, such as a brain aneurysm, and require immediate medical attention.
Secondary Headache
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comSecondary headache is a term used to describe headaches that are caused by an underlying medical condition, such as a brain tumor or infection. These headaches can be persistent and often require specialized care from medical professionals.
Cluster Headache Attack
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comCluster headache attack is a term used to describe the sudden onset of cluster headaches. These headaches typically come in clusters that can last for weeks or even months and often require medical intervention to manage.
Cervicogenic Headache
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comCervicogenic headache is a type of headache that is caused by a neck problem, such as a pinched nerve or muscle strain. These headaches can be challenging to manage and often require a combination of medications and lifestyle changes. Cervicogenic headaches can also come with additional symptoms, such as neck pain and stiffness.
Migraine Without Aura
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comMigraine without aura is a specific type of migraine that does not come with visual disturbances before the headache. Instead, individuals may experience a variety of symptoms, such as nausea, sensitivity to light and sound, and fatigue. Migraine without aura can be triggered by a variety of factors, including stress, hormonal changes, and certain foods.
Menstrual Migraine
Menstrual migraine is a type of migraine that is triggered by hormonal changes during a woman's menstrual cycle. These migraines typically occur before or during menstruation and can be challenging to manage. Hormonal therapies, such as birth control pills, may help reduce the severity of menstrual migraines.
Medication-Overuse Headache
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comMedication-overuse headache is a type of headache that is caused by overusing pain medications. This type of headache is often described as a constant, dull ache that is resistant to treatment. Managing medication-overuse headaches often involves slowly tapering off pain medications under the supervision of a medical professional.
Migraine Attack
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comMigraine attack is a term used to describe the onset and duration of a migraine headache. These attacks can last for several hours or days and often come with additional symptoms, such as nausea, sensitivity to light and sound, and visual disturbances.
Postdrome
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comPostdrome is a term used to describe the final, post-headache phase of a migraine. During this phase, individuals may experience a variety of symptoms, such as fatigue, mood changes, and difficulty concentrating. Recognizing the postdrome phase can help individuals better manage their migraines and take steps to prevent future attacks.
No comments:
Post a Comment